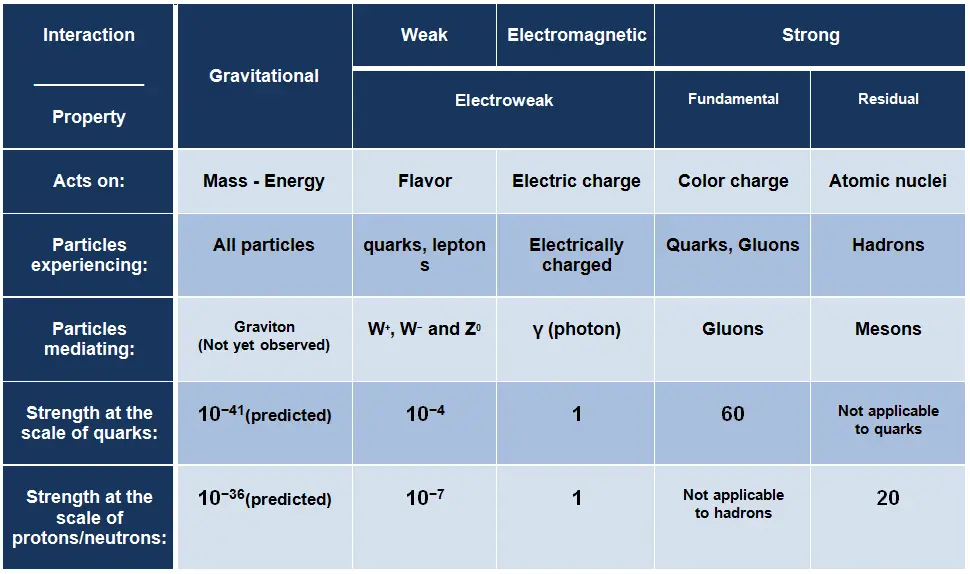
In physics, the fundamental interactions, also known as fundamental forces, are interactions among elementary particles that do not appear to be reducible to more basic interactions. These interactions govern how particles and also macroscopic objects interact and how certain particles decay. Generally, they can be classified into one of four fundamental forces:
Strong Interaction – Strong Force
The strong interaction or strong force is one of the four fundamental forces and involves the exchange of the vector gauge bosons known as gluons. In general, the strong interaction is very complicated interaction, because it significantly varies with distance. The strong nuclear force holds most ordinary matter together because it confines quarks into hadron particles such as the proton and neutron. Moreover, the strong force is the force which can hold a nucleus together against the enormous forces of repulsion (electromagnetic force) of the protons is strong indeed.
Weak Interaction – Weak Force
The weak interaction or weak force is one of the four fundamental forces and involves the exchange of the intermediate vector bosons, the W and the Z. Since these bosons are very massive (on the order of 80 GeV, the uncertainty principle dictates a range of about 10-18meters which is less than the diameter of a proton. As a result, the weak interaction takes place only at very small, sub-atomic distances. The weak interaction responsible for some nuclear phenomena such as beta decay, which can be understood in terms of the weak force operating on the quarks within the neutron.
Electromagnetic Interaction – Electromagnetic Force
The electromagnetic force is the force responsible for all electromagnetic processes. It acts between electrically charged particles. It is infinite-ranged force, much stronger than gravitational force, obeys the inverse square law, but neither electricity nor magnetism adds up in the way that gravitational force does. Since there are positive and negative charges (poles), these charges tend to cancel each other out. Electromagnetism includes the electrostatic force acting between charged particles at rest, and the combined effect of electric and magnetic forces acting between charged particles moving relative to each other.
Gravitational Interaction – Gravitational Force
Gravity was the first force to be investigated scientifically. The gravitational force was described systematically by Isaac Newton in the 17th century. Newton stated that the gravitational force acts between all objects having mass (including objects ranging from atoms and photons, to planets and stars) and is directly proportional to the masses of the bodies and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the bodies. Since energy and mass are equivalent, all forms of energy (including light) cause gravitation and are under the influence of it. The range of this force is ∞ and it is weaker than the other forces.
We hope, this article, Strong – Weak – Electromagnetic – Gravitational Force, helps you. If so, give us a like in the sidebar. Main purpose of this website is to help the public to learn some interesting and important information about radiation and dosimeters.