Nuclear decay (Radioactive decay) occurs when an unstable atom loses energy by emitting ionizing radiation. Radioactive decay is a random process at the level of single atoms, in that, according to quantum theory, it is impossible to predict when a particular atom will decay. During radioactive decay an unstable nucleus spontaneosly and randomly decomposes to form a different nucleus (or a different energy state – gamma decay), giving off radiation in the form of atomic partices or high energy rays. This decay occurs at a constant, predictable rate that is referred to as half-life. A stable nucleus will not undergo this kind of decay and is thus non-radioactive. There are many modes of radioactive decay:
-
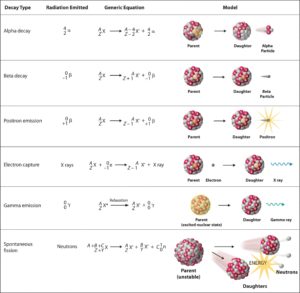
Notation of nuclear reactions – radioactive decays
Source: chemwiki.ucdavis.eduAlpha radioactivity. Alpha decay is the emission of alpha particles (helium nuclei). Alpha particles consist of two protons and two neutrons bound together into a particle identical to a helium nucleus. Because of its very large mass (more than 7000 times the mass of the beta particle) and its charge, it heavy ionizes material and has a very short range.
- Beta radioactivity. Beta decay is the emission of beta particles. Beta particles are high-energy, high-speed electrons or positrons emitted by certain types of radioactive nuclei such as potassium-40. The beta particles have greater range of penetration than alpha particles, but still much less than gamma rays.The beta particles emitted are a form of ionizing radiation also known as beta rays. The production of beta particles is termed beta decay.
- Gamma radioactivity. Gamma radioactivity consist of gamma rays. Gamma rays are electromagnetic radiation (high energy photons) of an very high frequency and of a high energy. They are produced by the decay of nuclei as they transition from a high energy state to a lower state known as gamma decay. Most of nuclear reactions are accompanied by gamma emission.
- Neutron emission. Neutron emission is a type of radioactive decay of nuclei containing excess neutrons (especially fission products), in which a neutron is simply ejected from the nucleus. This type of radiation plays key role in nuclear reactor control, because these neutrons are delayed neutrons.
We hope, this article, Radioactive Decay Mode, helps you. If so, give us a like in the sidebar. Main purpose of this website is to help the public to learn some interesting and important information about radiation and dosimeters.