Cosmic Radiation
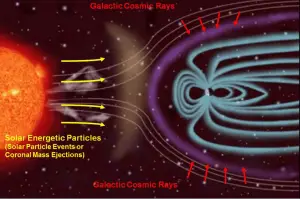 Cosmic radiation refers to sources of radiation in the form of cosmic rays that come from the Sun or from outer space. The earth has always been bombarded by high-energy particles originating in outer space that generate secondary particle showers in the lower atmosphere. Charged particles (especially high-energy protons) from the sun and outer space interact with the earth’s atmosphere and magnetic field to produce a shower of radiation (i.e. air shower), typically beta and gamma radiation. If you live at higher elevations or are a frequent airline passenger, this exposure can be significantly higher, since the atmosphere is thinner here. The effects of the earth’s magnetic field also determines the dose from cosmic radiation.
Cosmic radiation refers to sources of radiation in the form of cosmic rays that come from the Sun or from outer space. The earth has always been bombarded by high-energy particles originating in outer space that generate secondary particle showers in the lower atmosphere. Charged particles (especially high-energy protons) from the sun and outer space interact with the earth’s atmosphere and magnetic field to produce a shower of radiation (i.e. air shower), typically beta and gamma radiation. If you live at higher elevations or are a frequent airline passenger, this exposure can be significantly higher, since the atmosphere is thinner here. The effects of the earth’s magnetic field also determines the dose from cosmic radiation.
Shielding of Cosmic Radiation
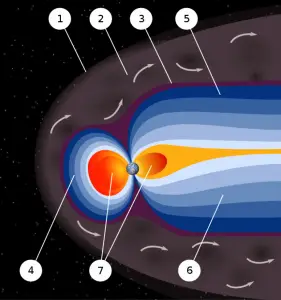
Earth’s magnetic field provides a vital radiation shield of cosmic radiation. In addition to a protective atmosphere, we are also lucky that Earth has a magnetic field. Magnetic field extends several tens of thousands of kilometers into space, protecting the Earth from the charged particles of the solar wind and cosmic rays that would otherwise strip away the upper atmosphere, including the ozone layer that protects the Earth from harmful ultraviolet radiation. It shields us from the full effects of the solar wind and GCR. Without this protection, Earth’s biosphere might not exist as it does today, or would be at least limited to the subsurface. Earth’s magnetic field provides also a radiation shield for astronauts and the ISS itself, because it is in low Earth orbit.
Calculations of the loss of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere of Mars, resulting from scavenging of ions by the solar wind, indicate that the dissipation of the magnetic field of Mars caused a near total loss of its atmosphere.
We hope, this article, Shielding of Cosmic Radiation, helps you. If so, give us a like in the sidebar. Main purpose of this website is to help the public to learn some interesting and important information about radiation and dosimeters.