One of three main types of detectors, which record different types of signals, is a counter. The activity or intensity of radiation is measured in counts per second (cps), which expresses a rate of counts per unit time as registered by a radiation monitoring instrument. In general, commonly used quantities are:
- counts per minute (cpm)
- counts per second (cps)
The best known counter is the Geiger-Müller counter. In radiation counters the generated signal from the incident radiation is created by the counting of the number of interactions occurring at the sensitive volume of the detector.
Unit of counts per second, which is detected by a device is somehow proportional to the activity of a measured sample. But note that, this proportionality is determined also by the distance between the detector and the sample and also by the detection efficiency.
What is one count
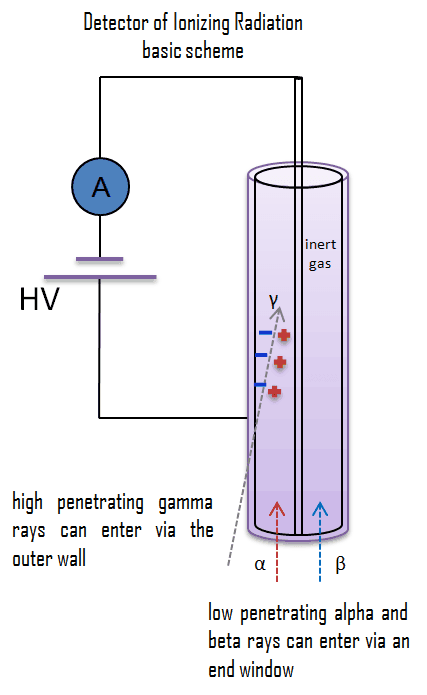
Let assume gaseous ionization detectors. Basic gaseous ionization detector consists of a chamber that is filled with a suitable medium (air or a special fill gas) that can be easily ionized. As a general rule, the center wire is the positive electrode (anode) and the outer cylinder is the negative electrode (cathode), so that (negative) electrons are attracted to the center wire and positive ions are attracted to the outer cylinder. The anode is at a positive voltage with respect to the detector wall. As ionizing radiation enters the gas between the electrodes, a finite number of ion-pairs are formed. Under the influence of the electric field, the positive ions will move toward the negatively charged electrode (outer cylinder), and the negative ions (electrons) will migrate toward the positive electrode (central wire). The collection of these ions will produce a charge on the electrodes and an electrical pulse across the detection circuit. However it is a small signal, this signal can be amplified, and then recorded as one count.
We hope, this article, Count per Second – CPS, helps you. If so, give us a like in the sidebar. Main purpose of this website is to help the public to learn some interesting and important information about radiation and dosimeters.