
Radiation dosimetry is the measurement, calculation and assessment of the absorbed doses and assigning those doses to individuals. It is the science and practice that attempts to quantitatively relate specific measures made in a radiation field to chemical and/or biological changes that the radiation would produce in a target.
External Dosimetry
External exposure is radiation that comes from outside our body and interacts with us. In this case, we analyze predominantly exposure from gamma rays and beta particles, since alpha particles, in general, constitute no external exposure hazard because the particles generally do not pass through skin. Since photons and beta interact through electromagnetic forces and neutrons interact through nuclear forces, their detection methods and dosimetry are substantially different. The source of radiation can be, for example, a piece of equipment that produces the radiation like a container with a radioactive materials, or like an x-ray machine. External dosimetry is based on measurements with a dosimeter, or inferred from measurements made by other radiological protection instruments.
Personal Dosimetry

Personal dosimetry is a key part of external radiation dosimetry. Personal dosimetry is used primarily (but not exclusively) to determine doses to individuals who are exposed to radiation related to their work activities. These doses are usually measured by devices known as dosimeters. Dosimeters usually record a dose, which is the absorbed radiation energy measured in grays (Gy) or the equivalent dose measured in sieverts (Sv). A personal dosimeter is dosimeter, that is worn at the surface of the body by the person being monitored, and it records of the radiation dose received. Personal dosimetry techniques vary and depend partly on whether the source of radiation is outside the body (external) or taken into the body (internal). Personal dosimeters are used to measure external radiation exposures. Internal exposures are typically monitored by measuring the presence of nuclear substances in the body, or by measuring nuclear substances excreted by the body.
Commercially available dosimeters range from low-cost, passive devices that store personnel dose information for later readout, to more expensive, battery operated devices that display immediate dose and dose rate information (typically an electronic personal dosimeter). Readout method, dose measurement range, size, weight, and price are important selection factors.
Protection against External Exposure
In radiation protection there are three ways how to protect people from identified external radiation sources:
-
Principles of Radiation Protection – Time, Distance, Shielding Limiting Time. The amount of radiation exposure depends directly (linearly) on the time people spend near the source of radiation. The dose can be reduced by limiting exposure time.
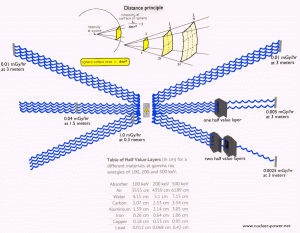
- Distance. The amount of radiation exposure depends on the distance from the source of radiation. Similarly to a heat from a fire, if you are too close, the intensity of heat radiation is high and you can get burned. If you are at the right distance, you can withstand there without any problems and moreover it is comfortable. If you are too far from heat source, the insufficiency of heat can also hurt you. This analogy, in a certain sense, can be applied to radiation also from radiation sources.
- Shielding. Finally, if the source is too intensive and time or distance do not provide sufficient radiation protection, the shielding must be used. Radiation shielding usually consist of barriers of lead, concrete or water. There are many many materials, which can be used for radiation shielding, but there are many many situations in radiation protection. It highly depends on the type of radiation to be shielded, its energy and many other parametres. For example, even depleted uranium can be used as a good protection from gamma radiation, but on the other hand uranium is absolutely inappropriate shielding of neutron radiation.
We hope, this article, External Dosimetry, helps you. If so, give us a like in the sidebar. Main purpose of this website is to help the public to learn some interesting and important information about radiation and dosimeters.